Dental X-rays
Children's X-rays
Today, dental radiography has become an indispensable tool for monitoring a patient's oral health.
It enables us to monitor the evolution of dental structure and anticipate problems (malformations, infections, pathologies, etc.). Thanks to a simple X-ray of the teeth, a dentist can detect abnormalities in good time and suggest appropriate treatment.
This dental examination uses a small amount of X-rays.
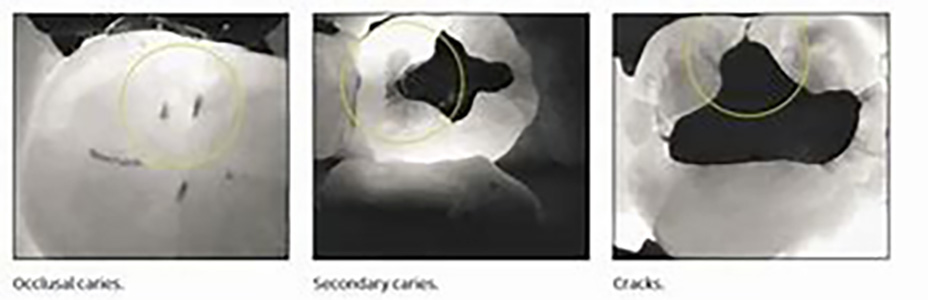
1 - Caries detection with and without X-rays
RETRO-CORONARY RADIOGRAPHY (OR BITE-WING)
It allows all caries to be seen between teeth or below the gum line. Their use has been shown in the literature to be more effective than clinical examination in detecting proximal lesions in dentine, estimating lesion depth and monitoring lesion behavior.
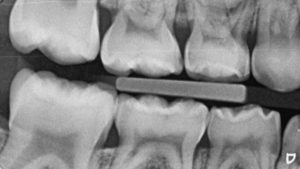
NO X-RAYS? DIAGNOCAM
The new KaVo DIAGNOcam is the first camera to use tooth structure to diagnose caries. It uses transillumination (laser) with a wavelength of 780nm, which is used like a fiber optic.
A digital camera takes the image and transfers it directly to the computer screen. Caries lesions will appear on the image as dark areas. Images can be saved, making patient follow-up much simpler. This system guarantees a better understanding of caries diagnosis.
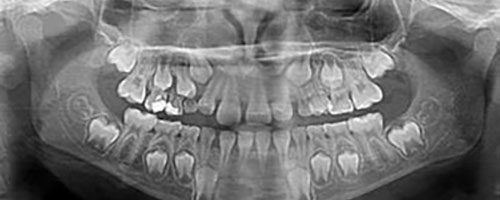
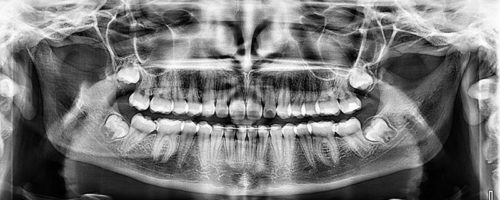
2 - Panoramic radiograph
In patients under the age of 20, including adolescents and children, teeth develop more rapidly. The type of dental X-ray should therefore be adapted to the patient's age:
- A panoramic X-ray between the ages of 6 and 8 to check for complete dentition;
- A panoramic X-ray between the ages of 10 and 13 to ensure that teeth are not crowded;
- A panoramic radiograph between the ages of 18 and 20 to monitor the growth of wisdom teeth.
Except in exceptional cases, dental X-rays are not necessary for children under 5.
Ideally, you should monitor your child's oral health from the age of 5 to detect any problems early and avoid complications.
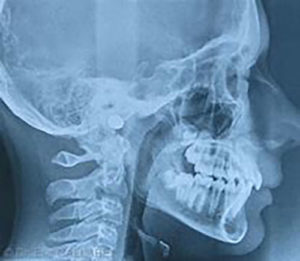
3 - Orthodontic diagnosis
PROFILE TELERADIOGRAPHY
Teleradiography is a radiological imaging technique that can be performed from the front and the side, allowing visualization of the entire skull. This examination, in addition to the dental panoramic, enables the orthodontist to identify various points of interest and measures necessary for certain orthodontic treatments.