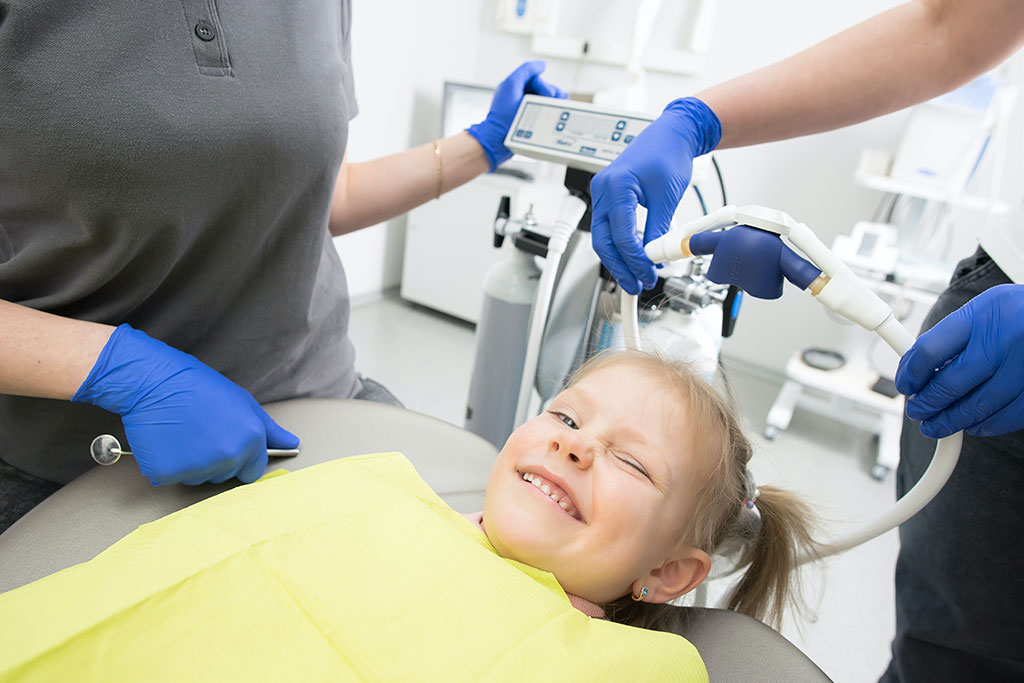
Conscious sedation and MEOPA
Sedation and general anesthesia
After many advances in the treatment and prevention of pain, dental care still generates feelings of anxiety in some children.
The stress induced by the fear of the unknown and especially the fear of pain is likely to modify the child's behaviour during care, which may alter the quality of the treatment or even compromise its completion.
What is MEOPA?
MEOPA, which stands for "Mixture of Equimolar Oxygen and Nitrous Oxide", is a colourless, odourless and tasteless gas that acts by inhalation.
Used for several years in hospitals, its use has been extended to dental practices to facilitate dental care.
This gas is inhaled through a suitable nasal mask, connected to a secure bottle. MEOPA does not put the patient to sleep, but allows the patient to relax: this is called "conscious sedation".
How is MEOPA used in the dental practice?
The use of MEOPA is generally intended for patients who are quite stressed, anxious, small and large, or for heavy and long procedures performed under local anaesthesia.
Before each treatment, a mask is placed over the patient's nose and mouth for several minutes. The patient is asked to breathe quietly and relax.
MEOPA has no side effects. It can only make you feel tingly and sometimes even laugh.
When the dental treatment begins, the mask is then placed only over the patient's nose and the patient continues to breathe calmly. It is therefore important not to have a cold on the day of the procedure.
The care is thus carried out in ideal conditions. The use of MEOPA does not replace local anaesthesia, which is carried out in the usual way.
Once the session is over, the patient remains seated and the effects of MEOPA wear off fairly quickly. MEOPA is an interesting alternative to general anaesthesia because the contraindications and side effects are much less important.
Conscious sedation for anxious children
Stressed patients with significant anxiety or oral hypersensitivity during treatment usually require treatment under general anaesthesia or conscious sedation.
Conscious sedation by inhalation of MEOPA is intended for all types of patients whose cooperation in the vigorous state is insufficient, i.e. young children with whom communication is difficult, anxious or phobic children and adolescents who often have memories of a previous painful medical or dental experience, and patients with special needs such as those with mental disabilities, cerebral palsy, autism, Down's syndrome, and multiple disabilities.
General anaesthesia at the Chêne-Bourg Dental Centre
Sedation is comparable to general anaesthesia in that certain reflexes of the body are retained. The safety measures are the same as for any general anaesthetic. Sedation is mainly used for medical investigations.
In an effort to provide appropriate dental care for all our patients, conscious sedation and MEOPA offer an additional level of treatment for your children.


